


What is Sustainability?
Sustainability is a broad concept that encompasses practices aimed at maintaining ecological balance, social equity, and economic prosperity. It revolves around “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”. Here are the key points:
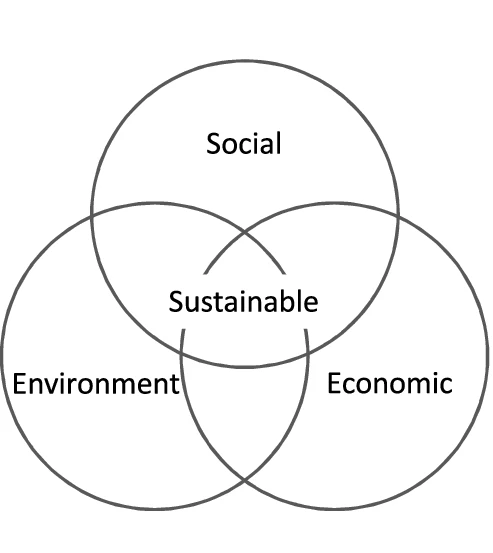
Sustainability considers three interconnected dimensions:
Environmental: Protecting natural resources, reducing pollution, and promoting conservation.
Social: Ensuring social well-being, equity, and inclusivity.
Economic: Balancing economic growth with responsible resource use.
Sustainable practices extend beyond profit-making to address societal and environmental challenges.
What is Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)


The United Nations’ SDGs provide a comprehensive framework and global goals for sustainable development. Key aspects:
The SDGs consist of 17 goals cover diverse areas, including poverty eradication, gender equality, climate action, and clean water access.
The aim is to achieve these goals by 2030 through collective global efforts.
Governments, businesses, and individuals all play a role in SDG implementation.
What is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
CSR represents an organization’s voluntary commitment to responsible business practices. CSR holds companies accountable for their impact on society and the environment. CSR encompasses various sustainable actions, such as:
Lowering carbon footprint
Investing in fair trade products
Engaging in volunteer work
Improving labour policies
Participating in charitable projects
By conducting CSR activities contributes to positive societal outcomes and enhances a company’s reputation.
ESG focuses on evaluating a company’s performance based on environmental, social, and governance factors. Key distinctions:
Environmental: Assessing a company’s impact on the environment, including carbon emissions, resource use, and waste management.
Social: Evaluating social practices, such as employee well-being, diversity, and community engagement.
Governance: Scrutinizing corporate governance structures, transparency, and ethical decision-making.
ESG ratings guide investors in making informed decisions aligned with sustainability goals.












You are about to enter a third party website and RHB Banking Group's privacy policy will cease to apply.
This link is provided for your convenience only, and shall not be considered or construed as an endorsement or verification of such linked website or its contents by RHB Banking Group.
RHB Banking Group also makes no warranties as to the status of this link or information contained in the website you are about to access.
PIDM Membership Representation

You are about to enter a third party website and RHB Banking Group's privacy policy will cease to apply.
This link is provided for your convenience only, and shall not be considered or construed as an endorsement or verification of such linked website or its contents by RHB Banking Group.
RHB Banking Group also makes no warranties as to the status of this link or information contained in the website you are about to access.
We used cookies to improve your experience on our website. By continuing to use our website and/or accepting this message, you agree to our use of cookies. Please refer to our Privacy Policy for more information.